
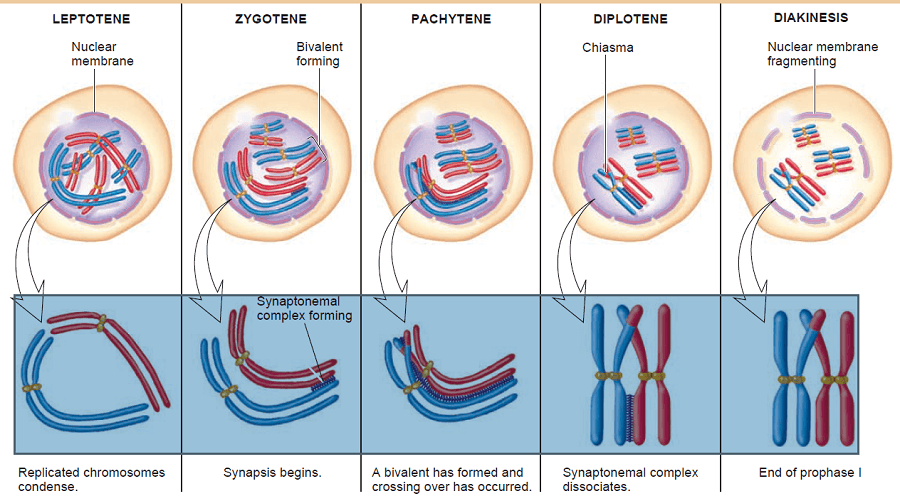
ANAPHASE II: chromatids separate to poles. METAPHASE II: chromosomes attach to spindle. TELOPHASE I: new nuclei form, in which there is only one type of each chromosome, although each is divided into two chromatids. ANAPHASE I: HOMOLOGOUS CHROMOSOMES separate to opposite poles. METAPHASE I: chromosomes migrate to the spindle equator to which they become attached by their CENTROMERES. PROPHASE I: homologous chromosomes pair, split into CHROMATIDS, and carry out CROSSING OVER. Further details of each stage can be obtained by referring to individual entries. Although meiosis is a continuous process it has been divided into numerous stages, given below. meiosis a type of nuclear division associated with sexual reproduction, producing four HAPLOID (1) cells from a single DIPLOID (1) cell, the process involving two cycles of division. This produces four haploid daughter cells with chromosomes composed of single chromatids.įig. Both daughter cells formed by meiosis I divide again and the two chromatids of each chromosome separate and go to separate daughter cells. Meiosis II then follows immediately without DNA replication. The assortment is random either the maternal or the paternal chromosome can go to a daughter cell.

Thus, each daughter cell receives the haploid number of chromosomes, each with two chromatids. The other phases of meiosis I and II resemble those of mitosis, except that in meiosis I the two chromosomes of each bivalent separate and move to opposite poles. In the last stage, diakinesis, the chiasmata move to the ends of the chromosomes. In the female, this stage (called dictyotene) is prolonged the oocyte remains in this stage from late fetal life until the time of ovulation.
During diplotene the two chromosomes of each bivalent separate except for X-shaped chiasmata where crossover has occurred. During this stage crossing over occurs, in which the chromatids of homologous chromosomes break and rejoin, resulting in chromatids that contain sections derived from both the mother and the father. The bivalent is now a tetrad of four chromatids. During pachytene the chromosomes thicken, and the chromatids of each chromosome separate except at the centromeres. The X and Y chromosomes synapse only at the ends of the short arms. This process is called synapsis and the structure formed is called a bivalent. During zygotene pairs of homologous chromosomes come into point-to-point contact along their length. During leptotene the chromosomes coil and contract each consists of two chromatids joined along their length. The first meiotic prophase is a complex process separated into five stages. As in mitosis (somatic cell division), meiosis I and II are each divided into four phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. There are two successive divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, in which four daughter cells that have the haploid chromosome number (23 in humans) are formed. The process of cell division by which reproductive cells (gametes) are formed.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
